
Integrating Generative AI into Workflows: Capabilities, Strategies, Best Practices and Examples
According to a 2024 survey by Gartner, 38% of HR leaders are currently using or planning to use generative AI tools and solutions in their organizations within the next 18 months (up from 19% in June 2023). This high and accelerating adoption rate highlights the growing importance of generative AI in transforming how HR departments operate.
But how can HR professionals effectively integrate this powerful technology into their existing workflows?
Generative AI, a subset of artificial intelligence capable of creating new content, ideas, and solutions, offers unprecedented opportunities for HR to streamline processes, enhance decision-making, and improve employee experiences. From automating routine tasks to providing personalized insights, the potential applications of generative AI in HR are vast and transformative.
However, the successful integration of generative AI into HR workflows isn’t just about implementing new technology. It requires a strategy, planning and a focus on building new capabilities within HR teams. How can HR departments navigate this transition effectively? What best practices should they follow to ensure seamless integration and maximize the benefits of generative AI?
This article explores the key strategies, real-world examples, and best practices for integrating generative AI into HR workflows.
We will explain the top essential capabilities HR teams need to develop, practical strategies for implementation, and insights from successful AI adoptions in HR processes.
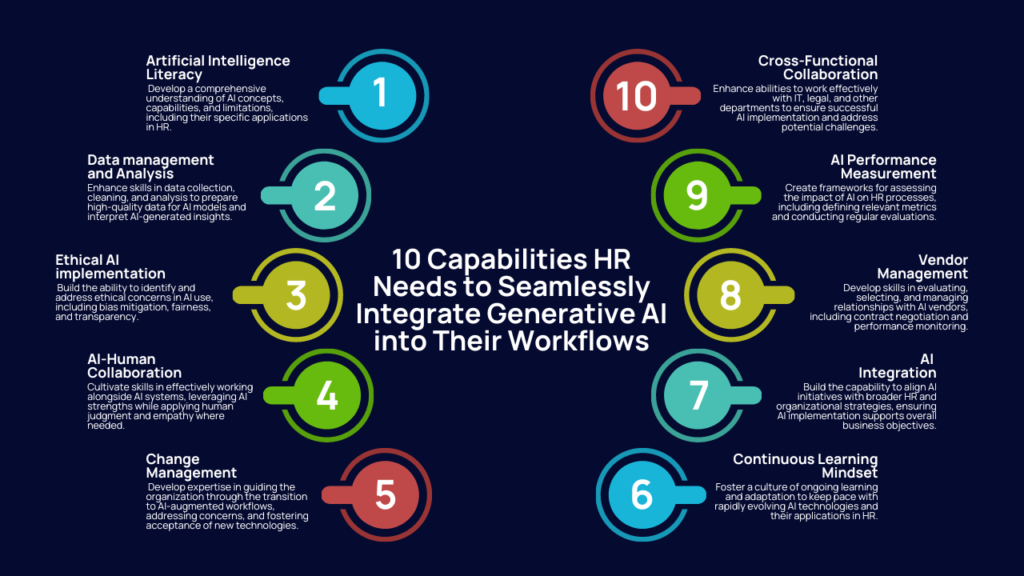
10 Capabilities HR Departments Need to Build to Seamlessly Integrate Generative AI into Their Workflows
These are ten essential capabilities HR teams should focus on:
- AI literacy: Develop a comprehensive understanding of AI concepts, capabilities, and limitations. This includes familiarity with different types of AI models (such as natural language processing, machine learning, and neural networks), their specific applications in HR, and the ability to critically evaluate AI solutions. HR professionals should be able to explain AI concepts to non-technical stakeholders and make informed decisions about when and how to apply AI in various HR processes.
- Data management and analysis: Enhance skills in data collection, cleaning, and analysis. This capability is fundamental for preparing high-quality data for AI models and interpreting AI-generated insights. HR teams should be proficient in data governance practices, understand the importance of data privacy and security, and be able to use data visualization tools to communicate insights effectively. They should also be capable of identifying potential biases in data sets and taking steps to mitigate them.
- Ethical AI implementation: Build the ability to identify and address ethical concerns in AI use, including bias mitigation, fairness, and transparency. This involves developing frameworks for responsible AI use in HR processes. HR professionals should be able to conduct ethical impact assessments for AI implementations, ensure AI decisions are explainable and fair, and develop policies that protect employee privacy and rights in an AI-augmented workplace.
- AI-human collaboration: Cultivate skills in effectively working alongside AI systems, understanding how to leverage AI strengths while applying human judgment and empathy where needed. This includes knowing when to rely on AI-generated insights and when human intervention is necessary. HR professionals should be able to design workflows that optimize the synergy between AI capabilities and human skills, ensuring that AI augments rather than replaces human decision-making in critical areas.
- Change management: Develop expertise in guiding the organization through the transition to AI-augmented workflows, addressing concerns, and fostering acceptance of new technologies. This involves creating comprehensive change management plans, effectively communicating the benefits and impacts of AI integration, and providing support and training to employees at all levels. HR teams should be skilled in identifying and addressing resistance to change and in creating a positive narrative around AI adoption.
- Continuous learning mindset: Foster a culture of ongoing learning and adaptation to keep pace with rapidly evolving AI technologies and their applications in HR. This includes staying updated on the latest AI trends, attending relevant conferences and workshops, and encouraging experimentation with new AI tools. HR departments should establish mechanisms for knowledge sharing and create learning paths for different roles within HR to ensure the entire team remains current with AI advancements.
- Strategic AI integration: Build the capability to align AI initiatives with broader HR and organizational strategies, ensuring AI implementation supports overall business objectives. This involves developing a deep understanding of the organization’s strategic goals and identifying areas where AI can create the most value. HR professionals should be able to create AI roadmaps that align with long-term organizational plans and articulate the strategic rationale for AI investments to senior leadership.
- Vendor management: Develop skills in evaluating, selecting, and managing relationships with AI vendors, including contract negotiation and performance monitoring. This includes the ability to assess vendor claims critically, understand the technical aspects of AI solutions sufficiently to make informed decisions, and negotiate contracts that protect the organization’s interests. HR teams should also be capable of managing ongoing vendor relationships, ensuring AI solutions continue to meet evolving organizational needs.
- AI performance measurement: Create frameworks for assessing the impact of AI on HR processes, including defining relevant metrics and conducting regular evaluations. This involves identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect the goals of AI implementation, such as time saved, accuracy improvements, or employee satisfaction. HR professionals should be able to design and implement monitoring systems, analyze AI performance data, and make data-driven decisions about refining or expanding AI use based on measured outcomes.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Enhance abilities to work effectively with IT, legal, and other departments to ensure successful AI implementation and address potential challenges. This includes developing a shared language around AI initiatives, understanding the perspectives and concerns of different stakeholders, and facilitating productive cross-departmental collaborations. HR teams should be skilled in project management, able to lead cross-functional AI implementation teams, and capable of navigating complex organizational dynamics to drive AI integration forward.
8 Strategies to Integrate Generative AI into HR Workflows
Read more HERE.